The role of fur or hair is to trap air near the skin in order to regulate body temperature. Unfortunately, ultrasound waves cannot pass through air. The fur must be clipped in order to obtain a clear picture.
Most pets require no sedation and lay quietly for the procedure.
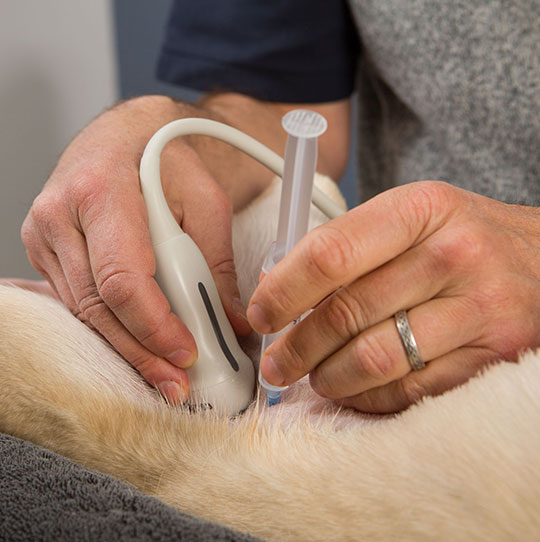
Especially nervous or wiggly patients may need sedation to enable a thorough examination. Sedation or brief anesthesia is usually employed if a biopsy or needle aspirate procedure is performed.
A fine needle aspirate (FNA) provides a sample of cells taken with a small gauge needle. This procedure may or may not require sedation.
A core biopsy (commonly referred to as a Tru-Cut biopsy) provides a tissue sample requiring a specialized large bore needle. This procedure is performed under general anesthesia to allow for accurate sampling and to reduce the risk of bleeding. We require a current coagulation profile prior to the procedure to ensure that the patient is able to clot appropriately.
A thoracic ultrasound is used to assess structures within the chest cavity. We may also evaluate blood flow to the chest organs.
An echocardiogram uses live ultrasound images to assess the function and structure of the heart for the specific purpose of assessing heart disease. While we usually briefly evaluate the heart during a thoracic ultrasound, it does not take the place of an echocardiogram.